| | | | db2db screenshots along with an overview of how to begin using the application:
|  Register jdbc drivers with the application here. Alternatively, drivers can be used if they are available on the classpath (see userconnection screenshot below). |  Create a userconnection, where a userconnection is a collection of details needed to connect to a DBMS e.g. username, password, the JDBC driver (as registered above). |  Set up a datatype mapping for each database you want to transfer tables to. db2db works by retrieving data and metadata from a database using JDBC datatypes. In order to create and populate tables in the target database it needs to maintain a mapping from these JDBC datatypes to equivalent types in the target database. As an example, the mappings are of the form:
decimal=decimal;decimal(1-28);decimal(1-28,0-28)
This indicates that the JDBC type decimal maps to the database specific type decimal. In addition, 0, 1 or 2 arguments may be used with a precision in the range 1-28 and a scale in the range 0-28. There are three ways to create this mapping:
 | db2db will query the JDBC driver and the target database to discover mappings. |
 | The user can enter the 'base type' (e.g. decimal) and db2db will discover the arguments allowed for that type (e.g. decimal(1-28);decimal(1-28,0-28)). |
 | The user can enter the complete mapping. |
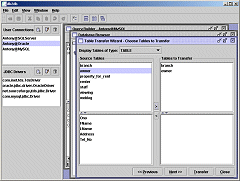 Now some tables can be copied from one database to another. A userconnection is chosen as the source database and another as the target database. Tables are chosen for transfer and the transfer is initiated. | 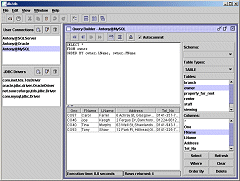 An SQL query builder allows SQL queries to be created, saved, opened and run against the database. |  The database browse shows information about the database: schemas, tables, table types, data, column datatypes, primary keys, referential integrity constraints, etc. | | | 
 |

